These first tools were bulky and needed several people to operate, making deployment at scale difficult. Arguably, the turning point came in the 1930s, when Dr Gerhard Fisher started his own company and successfully filed a patent for the “Metallascope” – a one-person operable metal detector that went on to lay the foundations for various key tools used by a diverse set of industries and fields today, ranging from checkpoint security, prospecting, and, of course, underground utility detection.

Active VS Passive
The modern underground utility electromagnetic locator (EML) consists of two major components – a receiver and a transmitter.
Unlike its counterparts in other industries, EMLs are capable of active detection on top of passive detection, because underground utilities usually have access points such as valves , and putting a current through the utility makes its location more apparent. Summarily:
Passive Detection Modes

Power
Electrical power systems in the world operate either at 50Hz or 60Hz. Modern EML receivers have a setting that is tailored to detect magnetic fields at these frequencies.
Radio
Radio waves emitted by various objects – satellites, cellular towers, radio stations, and the like – can be caught by metallic utilities and re-radiated as detectable signals. The frequency range of these signals is diverse, and modern EML receivers can either come with a preset of some of the more common frequencies or be adjustable in 1Hz or 5Hz steps.
Active Detection Modes
Direct Connection
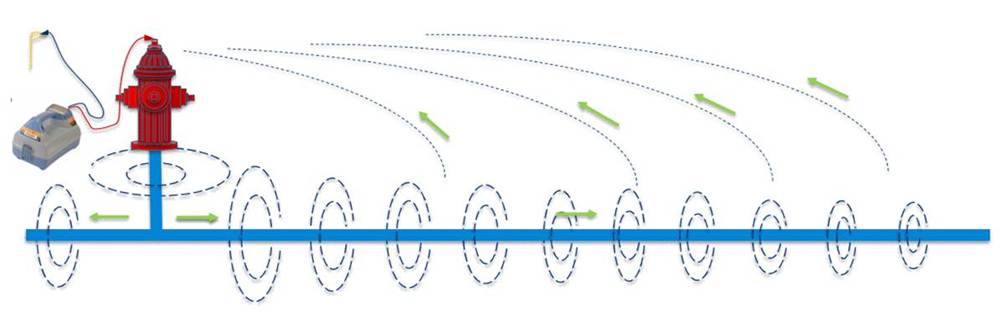
By attaching the red live lead of a modern EML transmitter directly to a utility at its access point and grounding the neutral black lead, a closed circuit is created through the utility that is to-be located. By choosing and setting a unique frequency for the transmitter, then matching it on the EML’s receiver, the utility can be distinguished from other buried objects in the area and more easily traced.

Signal Clamping

If creating a closed live circuit in the utility is not viable, a signal clamp can be attached to the throat of the utility and plugged into the EML’s transmitter. This will induce a signal on the utility to-be located at the chosen frequency and enable it to be detected on the paired EML receiver.
Induction
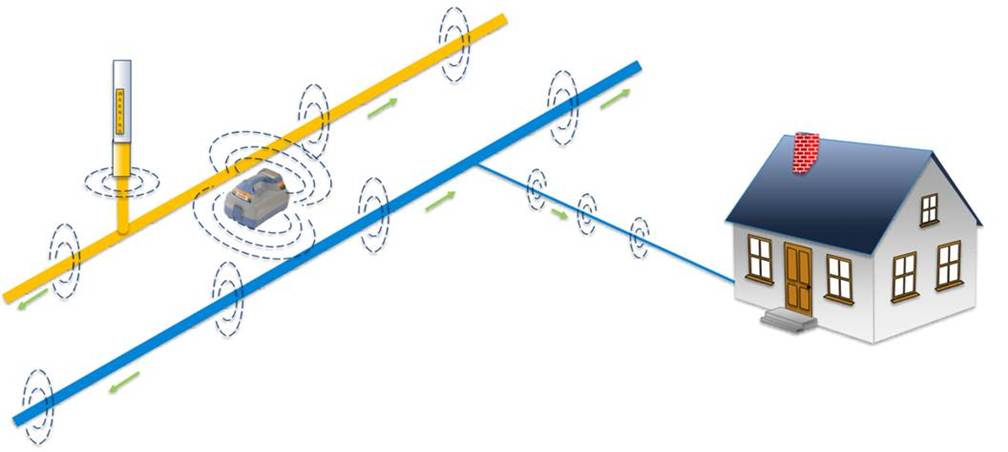
An EML transmitter can be placed near a utility’s access point and set to broadcast a signal at a specified frequency. Following the same principles as seen in the radio passive detection mode, the utility captures the signal and re-radiates it, enabling an EML receiver set to the same frequency to detect it.

Sonde
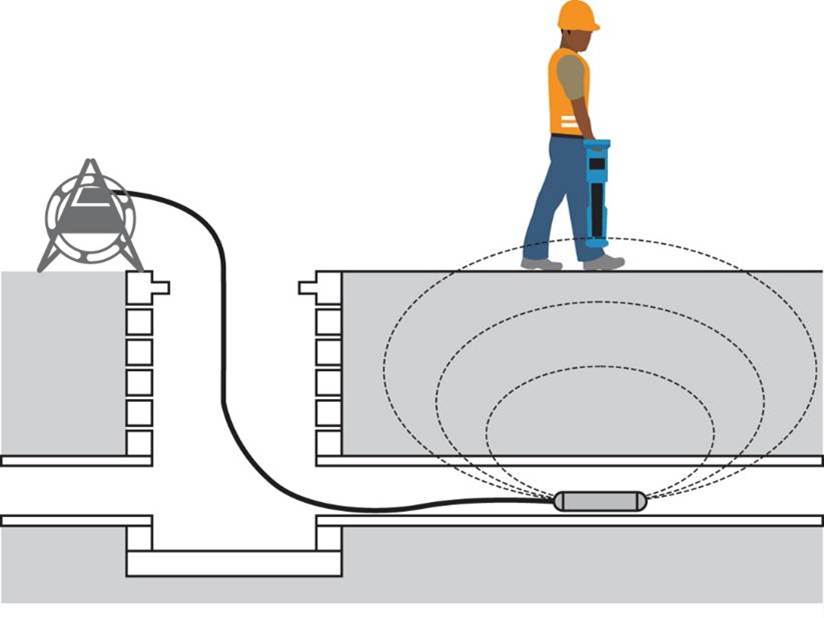
A sonde is a battery-operated miniature version of an EML’s transmitter. By tethering and inserting it into a utility to be pushed through, a matched EML receiver will be able to trace it above ground as it travels through the utility.
Law of the Instrument
EMLs are an integral part of any underground utility detection specialist’s toolkit. A compact design and intuitive feedback enable a single person to quickly canvas an area and check the state of what lies beneath. However, if it is not already apparent, EMLs work best with metallic, ferrous utilities. As more utilities are laid with non-conductive materials and composites today, it becomes increasingly challenging to map them with just EMLs alone. Even sending sondes through utilities present their own safety and logistical issues – stopping a live gas or water main for extended periods just to send a transmitter through it is sure to unduly disrupt surrounding communities and businesses.
Subsurface Utility Mapping Expertise
Dense urban environments like Singapore that constantly go through development and re-development produce a spaghetti-mess of utilities and installations underground, making it harder for EMLs to distinguish one thing from another. Here at GeoPulse Technologies, we understand that a more comprehensive approach is required to map the underground. We use Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) to complement EML when conducting non-invasive utility detection work, using each technology’s strengths to cover the other’s weakness. Before our boots fully hit the ground, we are also sure to investigate historical maps of the area’s subsurface and conduct as-is surveys of the area to check where access points of buried utilities are (occasionally, where they should be). If necessary, GeoPulse is also able to unearth underground utilities to show our clients visual proof of where their assets really are.
Once all this data is collected, we compile it into a Geo-Located Combined Utility Plan that you can use to make your decisions; where a new utility should go, how a new building and its foundations are laid, what civil infrastructure to build, and many other complex assessments. Remove a major complication to your works today. See the unseen. Contact us for a quote today.








 BR 32640
BR 32640  US 13835
US 13835  VN 6512
VN 6512  IN 5087
IN 5087  GB 2881
GB 2881  AR 2734
AR 2734  CN 2509
CN 2509  DE 1828
DE 1828 



