Article 3: BIM Four Dimensional for Underground Utilities BIM Technology
Article 3.1 What is BIM 4D?
4D Building Information Modelling (BIM 4D) refers to the integration of three-dimensional (3D) building models with time-related data to enable effective planning, scheduling, and monitoring of construction activities. In essence, 4D BIM adds the dimension of time, enabling stakeholders to perceive the progress of construction across the project’s lifecycle.
This integration facilitates dynamic simulations of construction sequences, enabling project teams to anticipate potential scheduling conflicts, optimize workflow, and improve site logistics. Through 4D BIM, project participants can assess the impact of schedule changes in literal real-time, enhance communication among stakeholders, and support decision-making processes by providing clear visual representations of the construction timeline.
By linking construction tasks to specific components in the digital model, 4D BIM supports more accurate planning, reduces delays, and contributes to overall project efficiency and risk mitigation.
Article 3.2 Advantages of 4D BIM in Underground Utilities

Enhanced Planning and Coordination
4D BIM enables the integration of time and spatial data, facilitating improved planning of underground utility networks. It helps coordinate the installation of various utility systems (e.g., Cable, water, sewer, gas, Telecom) to avoid conflicts and ensure optimal sequencing.
Clash Detection and Conflict Resolution
By visualizing the construction sequence in a time-based 3D environment, 4D BIM allows early detection of clashes between utility lines and existing infrastructure. This minimizes the risk of costly rework and construction delays.
Improved Scheduling and Time Management
The time-phased visualization of tasks allows project managers to optimize schedules, allocate resources efficiently, and monitor progress in real time. It helps identify potential bottlenecks in underground excavation and installation activities.
Risk Mitigation
Underground construction often involves unknown site conditions and high safety risks. 4D BIM helps simulate construction scenarios, allowing stakeholders to assess and mitigate risks before execution begins.
Better Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
The visual nature of 4D BIM models makes it easier to convey complex construction sequences to all stakeholders, including non-technical personnel. This enhances collaboration and supports informed decision-making.
Minimized Disruption to Surroundings
Detailed time-based planning allows for better management of construction impacts on nearby infrastructure, traffic, and residents. This is particularly important in urban environments where underground space is limited and highly congested.
Cost Efficiency
By reducing delays, preventing errors, and improving resource utilization, 4D BIM contributes to cost savings throughout the underground utility construction process.
Article 3.3 Comparison Between Traditional Methods and BIM 4D in Underground Utilities Construction
| Aspect | Traditional Method | BIM 4D Method |
| Project Planning | Relies on 2D drawings and separate schedules | Integrates 3D models with time schedules, enabling automated, visualized planning |
| Visualization | Limited to 2D technical drawings, difficult for non-experts to interpret | Provides dynamic, visual simulations of construction sequences, enhancing understanding for all stakeholders |
| Clash Detection | Clashes and conflicts often discovered during construction, causing delays | Identifies spatial and schedule-related clashes during design stage, reducing on-site issues |
| Scheduling | Static Gantt charts and CPM schedules with limited visualization | Time-linked 3D models allow real-time simulation and optimization of the construction schedule |
| Accuracy of Construction | Prone to human error due to manual interpretation of design and sequence | High accuracy through data-driven, automated visualization of sequencing and spatial constraints |
| Risk Management | Risks often identified late in the project lifecycle | Early identification and mitigation of construction and safety risks through simulation |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Limited engagement due to technical nature of documents | Improves engagement by providing intuitive, interactive models accessible to all parties |

Article 3.4 Who Does it Benefit?
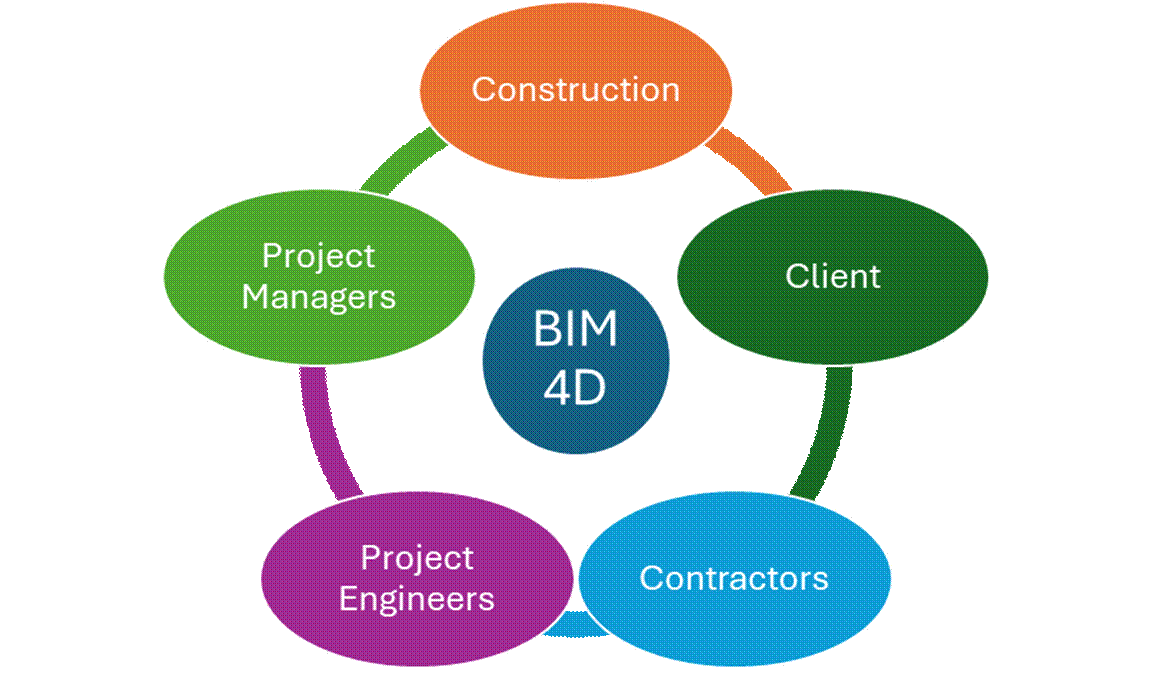
Construction Planners: Can transform the building process with higher precision.
Project Managers: It helps to figure out when to book equipment, buy materials and even hire a specialist if necessary.
Project Engineers: It prevents mistakes, defect clashes and adjust plans according to new information added.
Contractors: It improves project coordination and speed up the process for seamless results.
Client: With issues identified earlier and rectified at the source, clients enjoy cost and time savings.
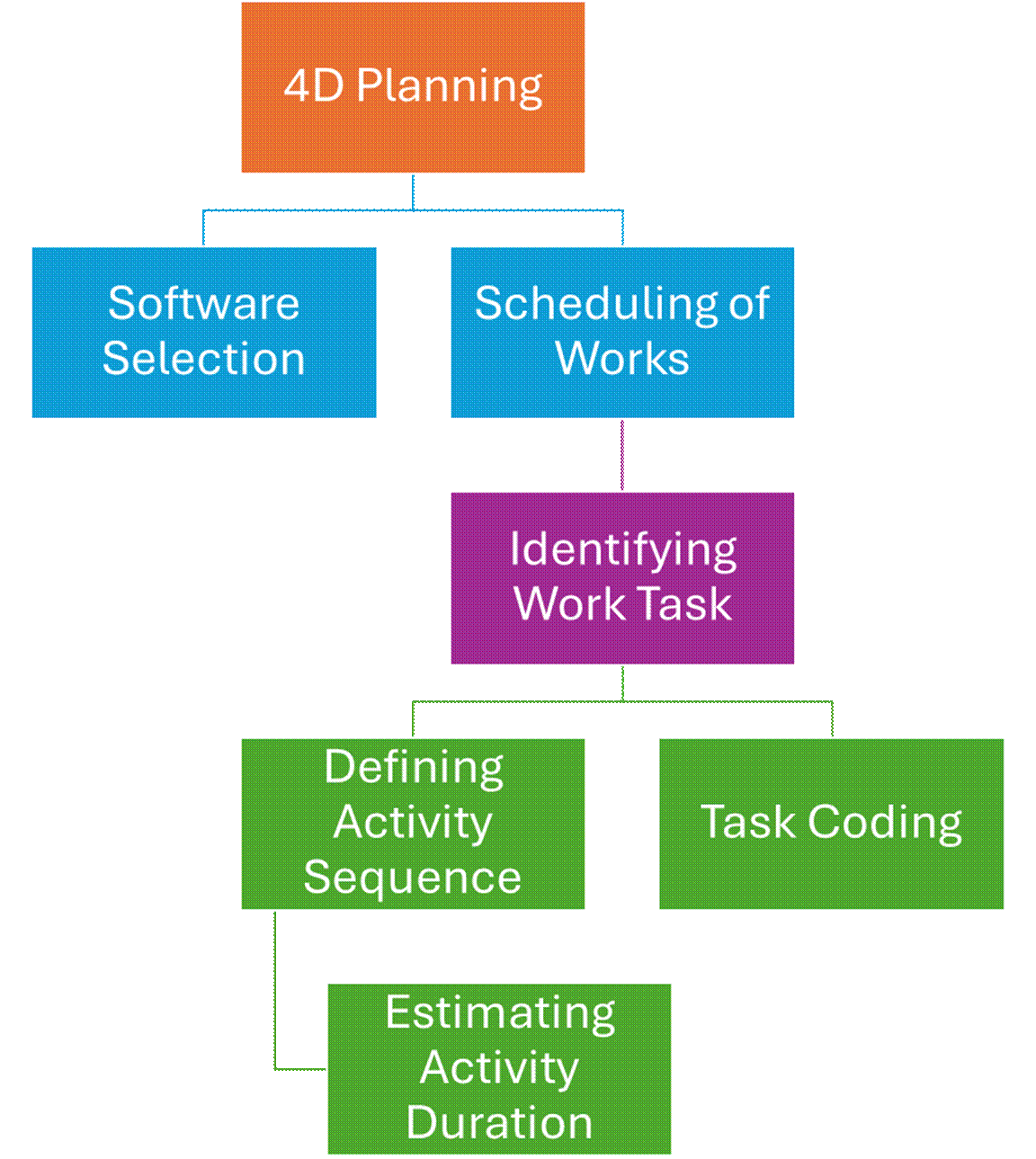
Article 3.5 Keys for 4D BIM Planning
Previous Article
Want more? Watch this!
.png)
Myat Kaung San is a Building Information Modelling Specialist that cut his teeth in the complex civil works of Singapore's underground infrastructure. He has recently moved to Canada seeking new horizons. Here's his linkedin and youtube.







 BR 32912
BR 32912  US 14158
US 14158  VN 4733
VN 4733  MX 3089
MX 3089  AR 2992
AR 2992  MY 2799
MY 2799  CN 2586
CN 2586  GB 2088
GB 2088 



