Introduction
Bearings are vital components in a wide range of industries, enabling smooth motion and reducing friction in machinery and mechanical systems. These small yet powerful devices play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, minimizing energy loss, and prolonging the lifespan of equipment. Without bearings, many essential applications—ranging from industrial production lines and transportation systems to medical devices and household appliances—would experience increased wear and inefficiency.
The versatility of bearings allows them to be adapted for various environments, from high-speed, high-load conditions in automotive and aerospace industries to precision-driven applications in robotics and healthcare. Different types of bearings, including ball bearings, roller bearings, and thrust bearings, are specifically designed to meet the needs of different sectors, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Bearings play a crucial role in multiple industries, ensuring efficient and smooth machinery operation. Key applications include:
- Motorcycles & Automotives – Bearings for engines, gearboxes, and wheel hubs.
- Aerospace & Aircraft – High-speed, heat-resistant bearings for jet engines and landing gear.
- Household Appliances – Bearings in washing machines, refrigerators, and vacuum cleaners.
- Agricultural Machinery – Heavy-duty bearings for tractors, irrigation systems, and harvesters.
- Railway – Bearings for wheel axle systems, traction motors, and suspension.
- Food Industry – Specialized hygienic bearings for processing and packaging machinery.
- Mining – Heavy-load bearings for drilling, crushing, and excavation equipment.
- Medical Equipment – Precision bearings in surgical tools, MRI machines, and wheelchairs.
1) Bearings for Motorcycles and Automotives
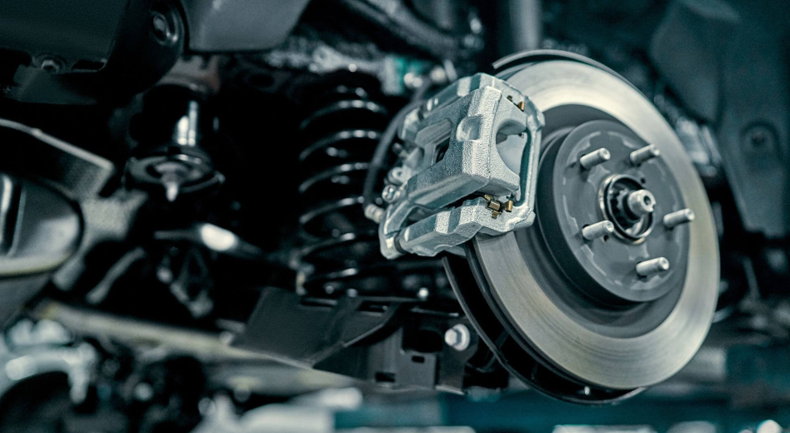
Bearings are vital components in motorcycles and automobiles, playing a critical role in reducing friction, ensuring smooth motion, and enhancing vehicle efficiency. As modern vehicles demand higher performance, fuel efficiency, and reliability, bearing technology continues to evolve with advanced materials, lubrication systems, and precision engineering.
Applications of Bearings in Motorcycles and Automotives
- Support wheel rotation while minimizing friction.
- Enhance driving stability, fuel efficiency, and vehicle lifespan.
- Common Types: Tapered roller bearings, deep groove ball bearings.
- Example: Sealed hub bearings in cars prevent contamination and require no maintenance.
- Bearings in camshafts, crankshafts, and connecting rods ensure smooth operation at high RPMs.
- Reduce friction in moving parts, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance.
- Common Types: Plain bearings, needle roller bearings, spherical bearings.
- Example: In high-performance motorcycles, ceramic-coated bearings provide enhanced durability.
3. Gearboxes_and_Transmissions
- Help transfer power efficiently by reducing wear in gears and shafts.
- Support high-speed rotation while handling heavy loads.
- Common Types: Cylindrical roller bearings, thrust ball bearings, deep groove ball bearings.
- Example: High-precision bearings in automatic transmissions improve gear-shifting smoothness.
- Bearings reduce steering resistance, enhancing handling and driving comfort.
- Provide shock absorption and stability in rough terrain.
- Common Types: Angular contact ball bearings, spherical roller bearings.
- Example: Motorcycles use tapered roller bearings in the steering head to maintain balance and control.
- Bearings support torque transmission and improve drivetrain efficiency.
- Reduce wear in high-torque applications such as performance cars and sports bikes.
- Common Types: Needle bearings, ball thrust bearings, cylindrical roller bearings.
- Example: High-load clutch release bearings improve smooth engagement in racing motorcycles.
- Bearings in alternators and starter motors ensure smooth and efficient operation of electrical components.
- Help maintain charging and ignition system performance.
- Common Types: Deep groove ball bearings.
- Example: Hybrid vehicles use high-speed bearings to optimize battery charging efficiency.
- Bearings in AC compressors and cooling fans enhance energy efficiency and durability.
- Reduce noise and vibration in climate control systems.
- Common Types: Ball bearings, needle bearings.
- Example: High-speed ball bearings improve the cooling efficiency in modern electric cars.
Key Benefits of High-Quality Bearings in Vehicles
Improved Fuel Efficiency – Reducing friction lowers energy loss and enhances mileage.Enhanced Durability and Performance – High-quality bearings withstand extreme heat, pressure, and speed.
Reduced Noise and Vibration – Precision engineering ensures smoother and quieter rides.
Higher Load Capacity – Essential for trucks, SUVs, and heavy-duty motorcycles.
Low Maintenance Solutions – Sealed and pre-lubricated bearings extend lifespan and reduce servicing costs.
Latest Trends in Automotive Bearings
- Reduce heat buildup, increase speed capability, and extend lifespan.
- Used in racing motorcycles and supercars.
- Designed for wheel hubs, transmissions, and suspension systems.
- Prevent contamination from dirt, water, and road debris.
2) Bearings for Aerospace and Aircraft

The aerospace industry demands bearings with exceptional durability, precision, and resistance to extreme conditions. These components must operate under high speeds, intense vibrations, temperature fluctuations, and even vacuum environments.
Applications of Bearings in Aerospace and Aircraft
1. Jet Engines
- Bearings in aircraft engines must withstand extreme temperatures and high-speed rotations.
- Ensure smooth operation of turbines and compressors.
- Common types:
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings – Handle both radial and axial loads in turbine shafts.
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings – Provide high load capacity in jet engine applications.
- Absorb heavy impact forces during takeoff and landing.
- Support smooth retraction and extension of landing gear.
- Common types:
- Tapered Roller Bearings – Support axial and radial loads under extreme pressure.
- Spherical Plain Bearings – Allow movement in multiple directions.
- Bearings in wing flaps, rudders, and ailerons enable precise movement and control.
- Used in actuators for landing gear and cargo bay doors.
- Common types:
- Thin Section Bearings – Reduce weight while maintaining high strength.
- Self-Lubricating Bearings – Minimize maintenance in hard-to-reach areas.
- Designed for vacuum environments with zero gravity.
- Must withstand extreme cold and heat cycles in space.
- Common types:
- Hybrid Ceramic Bearings – Provide low friction and high thermal resistance.
- Dry Film Lubricated Bearings – Operate without liquid lubrication in space.
Key Benefits of Aerospace Bearings
High Durability – Designed to function under extreme stress and fluctuating conditions.Lightweight Construction – Made from titanium, ceramic, and other advanced materials to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency.
Corrosion Resistance – Coated and treated to withstand harsh environmental exposure.
Low Maintenance – Self-lubricating and long-lasting designs reduce operational costs.
High-Speed Performance – Precision engineering ensures smooth and efficient operation in jet engines and navigation systems.
Latest Innovations in Aerospace Bearings
- Advanced Ceramic Bearings – Offer higher temperature resistance and lower weight for jet engines and spacecraft.
- Eco-Friendly Lubrication – New solid and self-lubricating materials reduce the need for liquid lubricants in aircraft.
- Smart Bearings with Sensors – Real-time monitoring for predictive maintenance in aircraft systems.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) – Producing complex, lightweight bearing designs for aerospace applications.
3) Bearings for Household and Appliances

Bearings play a crucial role in modern household appliances by ensuring smooth operation, reducing friction, and extending the lifespan of various machines. They enhance energy efficiency and contribute to quieter, more durable home devices.
Applications of Bearings in Household Appliances
1. Washing Machines
- Bearings support the drum’s rotation, ensuring smooth and stable movement.
- Withstand high-speed spinning and heavy loads.
- Common types:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings – Provide low-friction, high-speed performance.
- Sealed Bearings – Protect against water and detergent exposure.
- Bearings in compressors and fan motors help regulate cooling systems.
- Reduce energy consumption by minimizing mechanical resistance.
- Common types:
- Precision Ball Bearings – Support high-speed compressor functions.
- Self-Lubricating Bearings – Reduce maintenance needs.
- Bearings in the motor and rotating brushes ensure smooth operation.
- Enhance suction power and durability.
- Common types:
- Miniature Ball Bearings – Compact and high-speed for motor-driven components.
- Ceramic Bearings – Offer heat resistance and longer lifespan.
- Bearings reduce friction in motorized components, improving efficiency.
- Ensure stability and smooth operation under heavy loads.
- Common types:
- High-Speed Ball Bearings – Withstand rapid blade rotation.
- Sealed Bearings – Protect against food particles and moisture.
Key Benefits of Bearings in Household Appliances
Energy Efficiency – Reduces power consumption by minimizing mechanical resistance.Quieter Operation – Absorbs vibrations and reduces noise levels.
Increased Lifespan – Extends the durability of appliances through friction reduction.
Low Maintenance – Many bearings are self-lubricating and sealed to prevent wear.
Latest Innovations in Appliance Bearings
- Eco-Friendly Bearings – Designed with sustainable materials for energy savings.
- Noise Reduction Technology – Specially engineered bearings reduce vibrations in home appliances.
- Smart Bearings with Sensors – Enable predictive maintenance in high-end appliances.
- Compact and Lightweight Designs – Optimize space and efficiency in modern household gadgets.
4) Bearings in Agricultural Machinery

Agricultural machinery operates in harsh environments, requiring durable and high-performance bearings to withstand dirt, moisture, and heavy loads. Bearings play a vital role in ensuring the efficiency and longevity of farming equipment.
Applications of Bearings in Agriculture
1. Tractors and Harvesters
- Bearings support axles, transmissions, and hydraulic systems.
- Provide stability for high-load and high-speed operations.
- Common types:
- Tapered Roller Bearings – Handle heavy radial and axial loads.
- Self-Aligning Bearings – Compensate for misalignment on rough terrains.
- Bearings ensure smooth and efficient transport of harvested crops.
- Minimize downtime with self-lubricating designs.
- Common types:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings – Low-friction and high-speed performance.
- Sealed Bearings – Prevent contamination from dust and debris.
- Bearings in water pumps enable seamless motion and efficiency.
- Designed to resist water and corrosion.
- Common types:
- Stainless Steel Bearings – High resistance to moisture and chemicals.
- Ceramic Bearings – Excellent durability in wet conditions.
- Bearings enhance efficiency in soil preparation machinery.
- Handle extreme loads and continuous vibrations.
- Common types:
- Spherical Roller Bearings – Withstand heavy shock loads.
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings – Ideal for high-impact conditions.
Key Benefits of Bearings in Agriculture
Resistance to Harsh Conditions – Designed to endure dirt, moisture, and temperature extremes.High Load Capacity – Essential for heavy-duty farming machinery.
Extended Service Life – Reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
Improved Efficiency – Ensures smooth operation and fuel savings.
Latest Innovations in Agricultural Bearings
- Sealed & Self-Lubricating Bearings – Reduces maintenance in dusty and wet environments.
- Heavy-Duty Bearings with Shock Resistance – Enhances durability in rugged terrains.
- Smart Bearings with Sensors – Enables predictive maintenance to prevent equipment failure.
- Eco-Friendly Bearings – Designed with sustainable materials for greener farming.
5) Bearings in Railway

Railway systems rely on high-performance bearings to ensure safe, efficient, and long-lasting train operations. These bearings must withstand heavy loads, high speeds, and harsh environments, making durability and precision engineering essential.
Applications of Bearings in Railways
1. Wheel Axle Systems
- Bearings support the weight and motion of trains, ensuring smooth movement.
- Designed to handle radial and axial loads from high-speed operations.
- Common types:
- Tapered Roller Bearings – Support both radial and thrust loads.
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings – Provide high load capacity and durability.
- Bearings in traction motors help enhance efficiency in electric and diesel locomotives.
- Reduce friction and energy losses, improving power transmission.
- Common types:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings – Low friction for high-speed applications.
- Hybrid Ceramic Bearings – Lightweight and heat-resistant.
- Bearings absorb shocks and vibrations, ensuring passenger comfort and stability.
- Provide smooth suspension movement for high-speed rail systems.
- Common types:
- Spherical Roller Bearings – Withstand heavy loads and misalignment.
- Needle Roller Bearings – Ideal for compact suspension designs.
- Bearings reduce friction and wear in braking components.
- Improve braking response and safety in high-speed and freight trains.
- Common types:
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings – Handle combined radial and axial loads.
- Self-Lubricating Bearings – Minimize maintenance and improve reliability.
Key Benefits of Bearings in Railway
High Load Capacity – Engineered to support heavy-duty railway operations.Enhanced Durability – Resistant to continuous use, high-speed stress, and extreme conditions.
Reduced Maintenance & Downtime – Long service life improves train efficiency.
Noise & Vibration Reduction – Essential for passenger comfort and safety.
Latest Innovations in Railway Bearings
- High-Speed Rail Bearings – Optimized for faster and smoother train operations.
- Eco-Friendly & Energy-Efficient Bearings – Designed for reduced energy consumption.
- Smart Bearings with IoT Sensors – Enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Advanced Lubrication Technologies – Reduce wear and extend bearing lifespan.
6) Bearings in Food Processing
�earings_in_Food_Processing.png)
The food processing industry demands hygienic, corrosion-resistant, and high-performance bearings to ensure safety and efficiency in food production. Bearings in this sector must comply with strict sanitation regulations and withstand extreme temperatures, moisture, and cleaning chemicals.
Applications of Bearings in Food Processing
1. Conveyor Belts
- Bearings support smooth and efficient food transportation along production lines.
- Designed to resist contamination and frequent washdowns.
- Common types:
- Stainless Steel Bearings – High resistance to corrosion and chemicals.
- Sealed Ball Bearings – Prevent food particles from entering bearing components.
- Bearings enable smooth rotation in food processors, mixers, and blenders.
- Must withstand high-speed operation and repetitive movement.
- Common types:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings – Low friction for high-speed performance.
- Food-Grade Lubricated Bearings – Prevent contamination while ensuring longevity.
- Bearings ensure the precise movement of food packaging systems.
- Help maintain high-speed, automated operations with minimal maintenance.
- Common types:
- Self-Lubricating Bearings – Reduce the need for external lubrication.
- Plastic & Polymer Bearings – Lightweight and resistant to corrosion.
- Bearings operate in high-temperature ovens and cooling conveyors.
- Must withstand thermal expansion and rapid cooling cycles.
- Common types:
- Ceramic Bearings – Heat-resistant and non-reactive to food.
- Teflon-Coated Bearings – Non-stick and easy to clean.
Key Benefits of Bearings in Food Processing
Corrosion-Resistant Materials – Prevent rust and contamination in wet environments.Lubrication-Free or Food-Grade Lubricated Options – Maintain hygiene and safety standards.
Hygienic Design – Prevent food buildup and bacterial growth.
High Durability & Efficiency – Ensure long-lasting performance in harsh food processing conditions.
Latest Innovations in Food-Grade Bearings
- Heat-Resistant Bearings – Improve durability in high-temperature ovens.
- Self-Lubricating & Maintenance-Free Bearings – Enhance hygiene and reduce downtime.
- Antimicrobial Coated Bearings – Prevent bacterial contamination.
7. Bearings in Aviation

The aviation industry relies on high-precision, lightweight, and durable bearings to ensure aircraft safety, efficiency, and reliability. These bearings must withstand extreme temperatures, high loads, and intense vibrations while maintaining smooth operation in critical flight systems.
Applications of Bearings in Aviation
1. Flight Control Systems
- Bearings enable precise movement of flaps, rudders, and stabilizers for controlled flight.
- Must perform reliably in high-altitude and variable-pressure environments.
- Common types:
- Spherical Plain Bearings – Allow multi-directional movement with minimal friction.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings – Provide smooth and stable motion in control linkages.
- Support heavy impact loads during takeoff and landing.
- Designed to absorb shock and high-pressure stress.
- Common types:
- Tapered Roller Bearings – Handle both axial and radial loads efficiently.
- Self-Lubricating Bearings – Reduce friction and maintenance needs.
- Bearings in jet engines must operate at extreme speeds and temperatures.
- Reduce friction in compressors, turbines, and rotor shafts.
- Common types:
- High-Speed Ceramic Bearings – Provide heat resistance and extended lifespan.
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings – Support high-RPM operations with low noise.
- Bearings ensure smooth operation of airflow and climate control systems.
- Must be lightweight, quiet, and durable.
- Common types:
- Sealed Ball Bearings – Prevent dust contamination and ensure long service life.
- Polymer Bearings – Lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
Key Benefits of Bearings in Aviation
High Precision & Safety – Designed for mission-critical applications in aircraft.Resistance to Extreme Conditions – Withstand high temperatures, pressures, and vibrations.
Lightweight Materials – Improve fuel efficiency and aircraft performance.
Reduced Maintenance – Self-lubricating options lower the need for frequent servicing.
Latest Innovations in Aviation Bearings
- Hybrid Ceramic Bearings – Offer superior heat resistance and durability.
- Self-Lubricating & Maintenance-Free Bearings – Reduce downtime and servicing costs.
- Magnetic & Electromechanical Bearings – Improve efficiency in next-gen aircraft engines.
- Eco-Friendly, Low-Friction Bearings – Enhance sustainability in aviation.
8) Bearings in Medical Equipment

The medical industry depends on high-precision, reliable, and hygienic bearings to ensure smooth operation, accuracy, and patient safety. These bearings must withstand continuous use, high-speed motion, and strict sterilization requirements while maintaining low noise and minimal friction for medical applications.
Applications of Bearings in Medical Equipment
1. MRI and CT Scanners
- Bearings enable the smooth and silent rotation of imaging systems.
- Must be non-magnetic to function safely in MRI environments.
- Common types:
- Ceramic Bearings – Non-magnetic and heat-resistant.
- Precision Ball Bearings – Allow high-speed, vibration-free motion.
- Bearings enhance precision and stability in robotic-assisted surgery.
- Designed for high accuracy and smooth articulation.
- Common types:
- Miniature Bearings – Used in small surgical tools for fine movements.
- Angular Contact Bearings – Provide precise multi-directional motion.
- Bearings improve mobility, comfort, and adjustability.
- Must be lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant.
- Common types:
- Sealed Ball Bearings – Prevent dust and fluid contamination.
- Polymer Bearings – Lightweight and self-lubricating for smooth motion.
- Bearings support high-speed rotation for accuracy and efficiency.
- Require low-friction operation for reduced heat and noise.
- Common types:
- High-Speed Ceramic Bearings – Heat-resistant for extended use.
- Hybrid Bearings – Combine metal and ceramic for optimal performance.
Key Benefits of Bearings in Medical Equipment
High Precision & Reliability – Essential for accurate medical procedures.Corrosion-Resistant & Hygienic – Designed for sterile and long-lasting performance.
Low-Friction & Silent Operation – Reduces noise and vibration for patient comfort.
Lightweight & Durable – Enhances ease of use and longevity in medical devices.
Latest Innovations in Medical Bearings
- Miniature & Ultra-Precision Bearings – Enhance robotic surgery accuracy.
- Self-Lubricating Bearings – Reduce maintenance in hospital equipment.
- Antibacterial Coated Bearings – Improve hygiene in medical devices.
- Smart Bearings with Sensors – Enable real-time diagnostics and predictive maintenance.
9) Bearings in Mining

The mining industry demands heavy-duty, high-performance bearings that can withstand harsh environments, heavy loads, and extreme temperatures. Bearings play a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency, durability, and safety of mining operations.
Applications of Bearings in Mining
1. Drilling Equipment
- Bearings enhance the efficiency and precision of rock drilling and mineral extraction.
- Must withstand intense vibrations and high impact forces.
- Common types:
- Tapered Roller Bearings – Handle heavy axial and radial loads.
- Thrust Bearings – Provide support for high-pressure drilling applications.
- Bearings ensure smooth transportation of coal, minerals, and ores over long distances.
- Designed for continuous operation with minimal maintenance.
- Common types:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings – Provide low friction and high-speed performance.
- Sealed & Shielded Bearings – Prevent dust and debris contamination.
- Bearings support the movement of heavy-duty crushers that break down large rocks and ores.
- Require shock-resistant designs to handle extreme loads.
- Common types:
- Spherical Roller Bearings – Absorb shock loads in crushers.
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings – Withstanding heavy radial loads in ore processing.
- Bearings enable the smooth articulation and movement of mining excavators and loaders.
- Designed to function in muddy, dusty, and abrasive conditions.
- Common types:
- Self-Lubricating Bearings – Reduce wear and extend service life.
- Needle Roller Bearings – Provide compact, high-load capacity for moving parts.
Key Benefits of Bearings in Mining
Extreme Durability – Withstands heavy loads, shocks, and high temperatures.Resistance to Dust & Debris – Sealed designs prevent contamination in mining environments.
Heavy-Duty Load Capacity – Essential for large-scale industrial machinery.
Reduced Downtime – Increases efficiency and profitability in mining operations.
Latest Innovations in Mining Bearings
-
Self-Lubricating Bearings – Extend service life in dusty conditions.
- High-Temperature Bearings – Designed for harsh underground environments
- Smart Bearings with Sensors – Enable real-time condition monitoring.
- Eco-Friendly & Energy-Efficient Bearings – Reduce mining’s environmental impact.
Future Trends in Mining Bearings
The mining industry is shifting towards automation and predictive maintenance, increasing the demand for longer-lasting, self-monitoring bearings. Future advancements will focus on wear-resistant materials, AI-powered diagnostics, and energy-efficient designs to enhance operational efficiency and sustainability.Bearings are a vital component in almost every industry, from transportation and agriculture to aerospace and medical applications. Their ability to reduce friction, improve efficiency, and enhance the lifespan of machinery makes them indispensable across various sectors. With ongoing advancements in bearing technology, industries continue to benefit from enhanced performance, durability, and sustainability.
10) Bearing for Paper Making Machinery

The paper-making industry relies on high-performance bearings to ensure smooth and efficient operation under demanding conditions such as high speeds, elevated temperatures, and continuous moisture exposure. Bearings play a vital role in rolling, unwinding, slitting, and rewinding paper materials throughout the production process.
Key Applications of Bearings in Paper Machinery
1. Paper Rolling and Unwinding
- Bearings support large paper rolls as they unwind for further processing.
- Common types:
- Spherical Roller Bearings – Handle both radial and axial loads.
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings – Ideal for heavy loads and high-speed operation.
- Bearings ensure high-speed and precision cutting of paper into required sizes.
- Common types:
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings – Provide smooth and precise rotation.
- High-Speed Deep Groove Ball Bearings – Reduce friction for efficient slitting and rewinding.
- Bearings operate in high-temperature environments and support heavy loads.
- Common types:
- Heat-Resistant Spherical Roller Bearings – Withstand continuous high temperatures.
- Self-Aligning Bearings – Compensate for shaft deflection under heavy loads.
- Bearings help in polishing and smoothing the paper surface.
- Common types:
- Tapered Roller Bearings – Offer high load capacity and durability.
- Sealed Bearings – Protect against moisture and contaminants.
Challenges & Solutions for Bearings in Paper Making
High Temperatures & Humidity → Use heat-resistant and moisture-sealed bearings.Continuous Heavy Loads → Opt for high-load-capacity roller bearings.
Shaft Deflection & Misalignment → Use self-aligning bearings for compensation.
Early Abrasion & Creep → Implement special coatings and high-performance lubricants.
Inner Ring Fracture → Choose durable materials and precision-engineered designs.
Key Benefits of Bearings in Paper Production
Extended Service Life – Reduces downtime and maintenance costs.Enhanced Durability – Designed to withstand heat, moisture, and high loads.
High-Speed Performance – Ensures efficient paper processing.
Low Friction & Energy Efficiency – Improves machine reliability and output.
Latest Innovations in Paper Machinery Bearings
- Self-Lubricating Bearings – Reduce manual lubrication and maintenance.
- Hybrid Ceramic Bearings – Improve heat and corrosion resistance.
- Condition Monitoring Sensors – Detects early wear and prevent unexpected failures.
Conclusion: Bearings in Different Industries and Applications
Bearings are fundamental to the smooth operation of countless industries, providing stability, efficiency, and durability in machinery. Their versatility allows them to be used in everything from industrial manufacturing to aerospace applications. As technology advances, the development of high-performance bearings will continue to enhance productivity, reduce maintenance costs, and support innovation across various fields.







 US 7196
US 7196  BR 3242
BR 3242  CA 1658
CA 1658  AU 1602
AU 1602  TH 1516
TH 1516  JP 1428
JP 1428  SG 1231
SG 1231  VN 973
VN 973 

