Laser Alignment on Rotating Equipment
Accurate alignment is one of the most critical factors in maintaining the performance and reliability of rotating machinery. Laser alignment ensures that two or more shafts are properly positioned relative to each other, minimizing vibration, bearing wear, and energy loss.
Understanding Laser Alignment
Laser alignment is a precision method used to align the shafts of motors, pumps, compressors, fans, or other coupled machines. Unlike traditional dial indicator or straightedge methods, a laser alignment system provides fast and highly accurate readings by using laser transmitters and digital sensors to detect even the smallest misalignments.
Types of Misalignment
Rotating equipment typically experiences two main types of misalignment:
- Offset Misalignment: The shafts are parallel but not collinear, creating an offset between their centers.
- Angular Misalignment: The shafts are at an angle to each other, meaning they are not parallel.
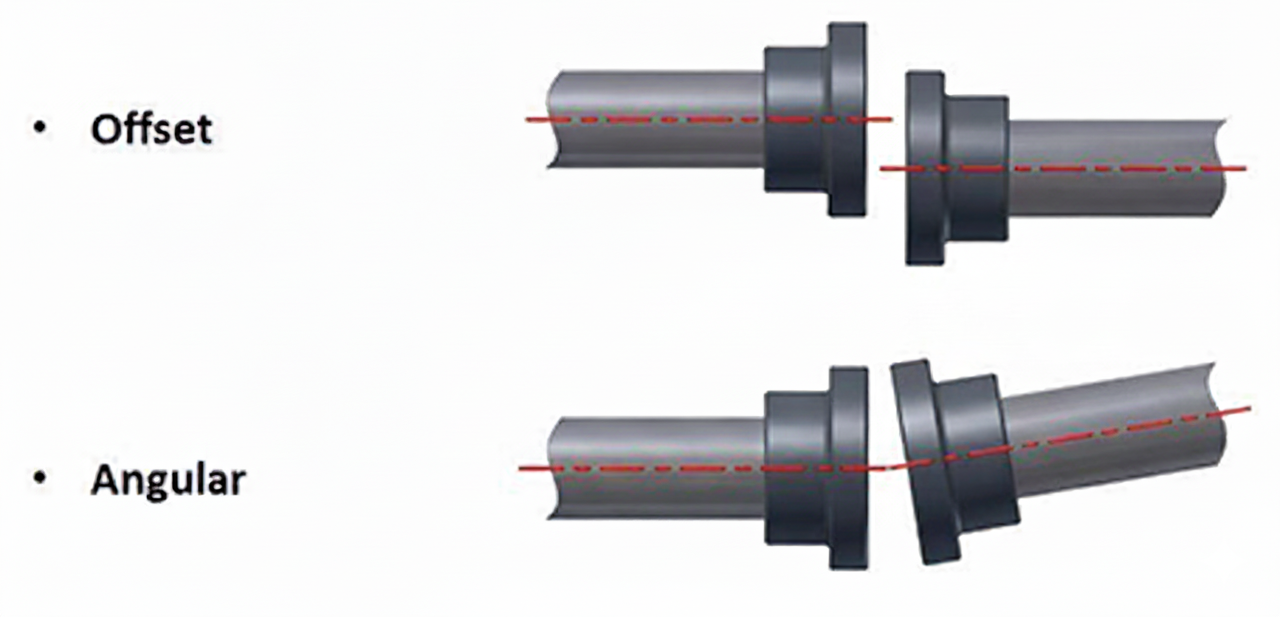
Both types can occur in horizontal or vertical planes, and laser systems can detect and quantify each with precision.
Procedure of Laser Alignment
The laser alignment process generally involves the following steps:
- Preparation: Ensure both machines are mounted and bolts are tightened uniformly. Clean the coupling surfaces and check for runout or looseness.
- Setup: Attach the laser sensors and brackets to both shafts or couplings according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Measurement: Rotate the shafts through specified positions (usually 9, 12, and 3 o’clock) to record alignment readings.
- Adjustment: Use shims and lateral adjustments to correct horizontal and vertical misalignments as indicated by the laser display.
- Verification: After adjustments, remeasure to confirm that alignment is within the specified tolerance.
Benefits of Laser Alignment
- Reduces vibration and noise.
- Prevents premature bearing and seal failure.
- Improves energy efficiency and performance.
- Extends equipment lifespan.
- Reduces maintenance costs and downtime.
Common Applications
Laser alignment is widely used across various industries including:
- Power generation
- Cement Industry
- Palm Oil Mill
- Water treatment plants
- Steel Industry
- Manufacturing and process industries
- Oil & gas facilities
- HVAC systems
Conclusion
Proper alignment using laser technology is a key part of predictive maintenance and reliability-centered practices. By performing laser alignment on rotating equipment, companies can achieve smoother operation, reduce downtime, and ensure optimal performance of their machinery.







 BR 19018
BR 19018  VN 9361
VN 9361  AR 1833
AR 1833  CN 1625
CN 1625  US 1364
US 1364  MY 1130
MY 1130  EC 856
EC 856  SG 785
SG 785 

